Recurrent Networks
Recurrent Networks
Usage
- Used to predict a sequence of inputs
- Speech recognition
- Time series prediction
- Machine translation
- Handwriting recognition
NetTalk
- Sliding window - window of 7 characters (input), predict the pronunciation of the middle input
- 26 output units representing the alphabet
- Can only learn short term dependencies
Simple recurrent network
- Simple recurrent network
- At each time step, hidden layer activations copied to a ‘context’ layer
- Hidden layer receives connections from input and context layers
- Context layer retains state information for indefinite period of time
- Backpropogation is done through time - recurrent
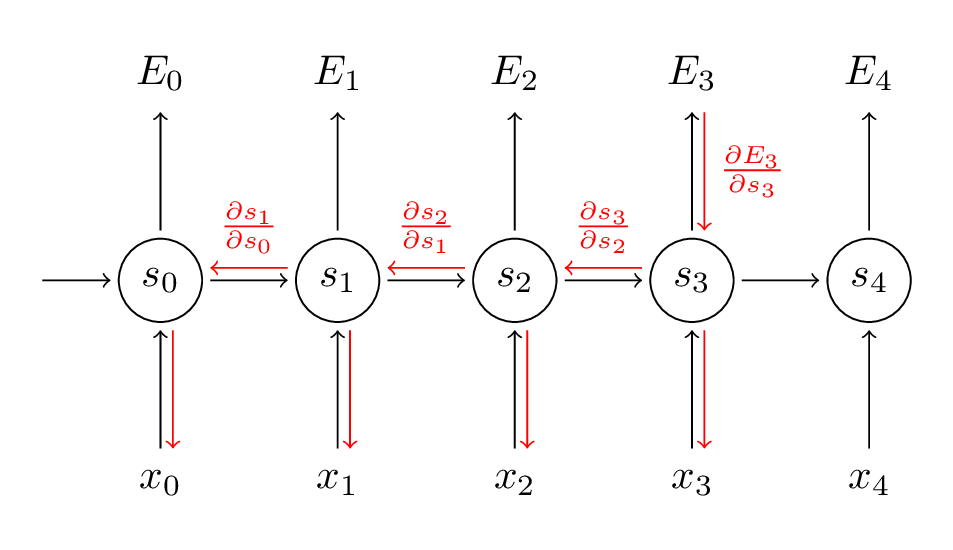
- Second order network - have two (or more) sets of weights and switch between them
- Also called gated - could have a weight of 0 and weight of 1
Finite State Machine
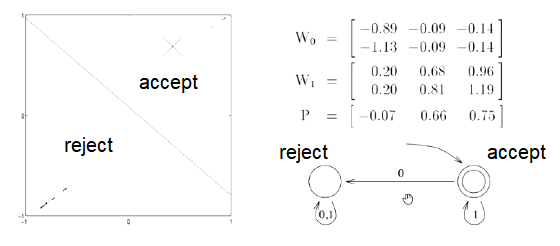
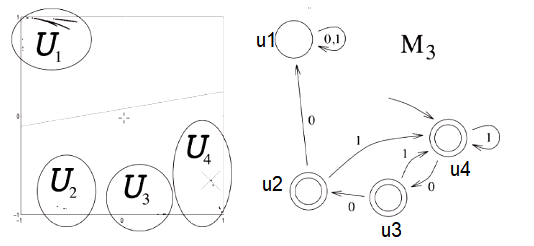
As they are trained, the points/areas move apart.
Chomsky Hierarchy:
| Language | Machine | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regular | Finite State Automation | $a^n\space (n\space odd)$ |
| Context Free | Push Down Automation | $a^n b^n$ |
| Context Sensitive | Linear Bounded Automation | $a^nb^nc^n$ |
| Recursively Enumerable | Turing Machine | true QBF |
- Formal Language Prediction: predict next character/word in the sequence.
- Elman Network
- Predict next after abaabbaaabbb…
- Line to separate classes
Long Range Dependencies
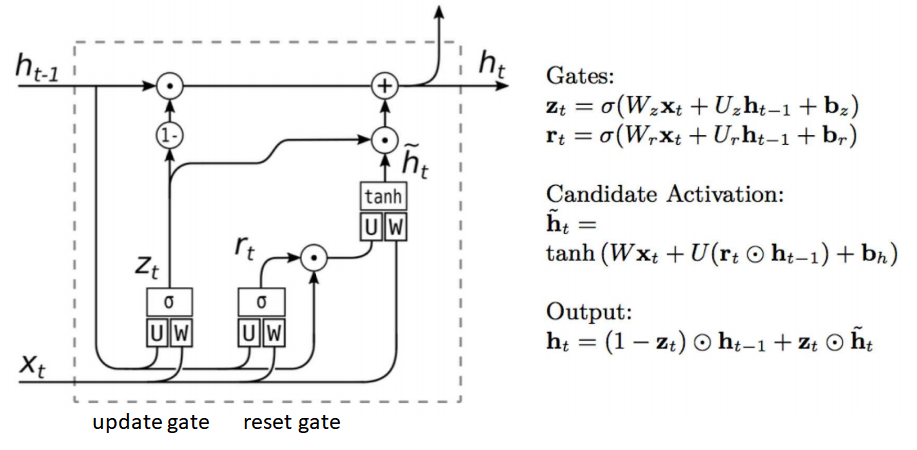
- Long Short Term Memory (LSTM)
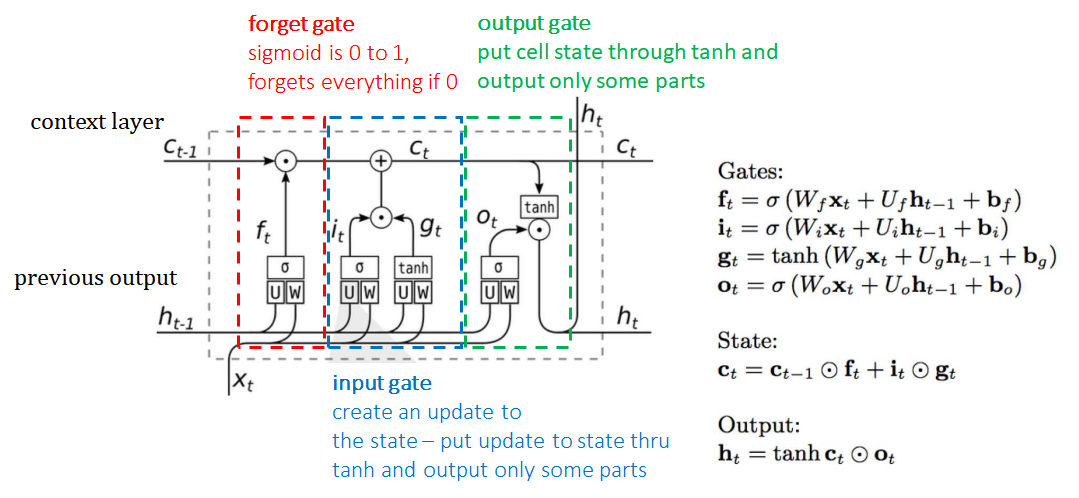
- Gated Recurrent Units (GRU)